Accessibility Issues and strategies for people with learning disabilities
According to the UK Government learning disabilities are defined as having ‘a significantly reduced ability to understand new or complex information, to learn new skills (impaired intelligence), with a reduced ability to cope independently (impaired social functioning), which started before adulthood’.
Learning disabilities can have a wide range of effects depending on the severity of the disability but in terms of digital accessibility people with learning disabilities can have:
- Difficulty reading and writing
- Difficulty understanding complicated information
- Difficulty with memory
- Communication difficulties
Although as stated previously the terms ‘Learning Difficulty’ and ‘Learning Disability’ tend to be used interchangeably they are different conditions. Learning difficulties may affect only one activity (eg reading and writing) with no other impairment of intellect. Learning disabilities. on the other hand, will have a more wide ranging affect on many activities and will affect intellect. People with learning disabilities can also have learning difficulties. We will now look at some of the issues people with learning disabilities face accessing digital information and the strategies which can help mitigate these issues.
- Reading and writing. Screen Readers are a useful tool for people with learning disabilities who may have difficulty reading text on a screen and can find them helpful when typing their own text
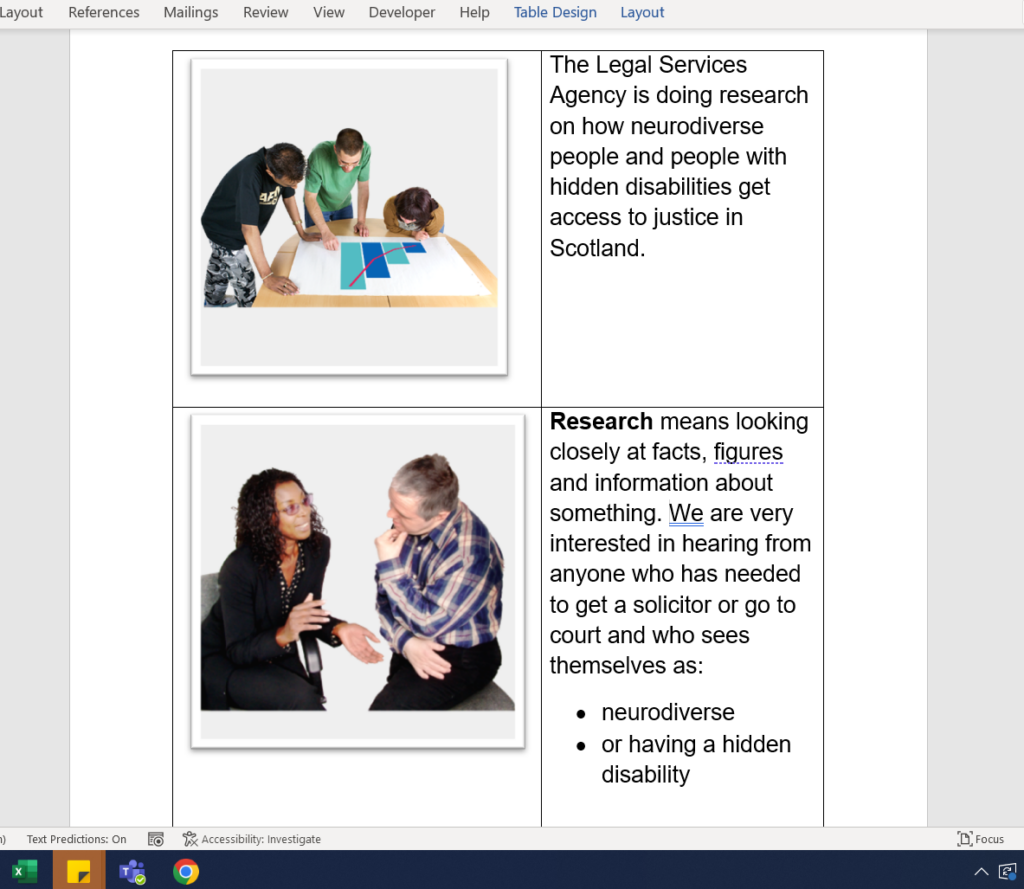
- Complex writing style. Information which is complex or written in an oblique style (sarcasm, satire, overly jargony etc) can prove challenging for people with learning disabilities. One common strategy is to employ a system called Easy Read when you are writing online content or documents. Easy Read is a writing style where you break down your text content into short, simple sentences along with descriptive pictures at the left. It looks like this.
- Easy Read documents can be made from your original documents by organisations such as Disability Equality Scotland. Disability Equality Scotland also run training courses in how to produce your own Easy Read documents. There will be a link to them in the Additional Resources page at the end of this training. If Easy Read is not an option then content providers may consider keeping sentences short and simple and kept as jargon free as possible. alternatively content providers could produce different versions of their content with one version being simple text.
- Complex menu systems. Menu systems on websites and apps could also be kept as simple and linear as possible making it easier for everyone to navigate their way through a website to the information they need.
- Cluttered pages. People with learning difficulties may also have issues understanding online content which is busy and cluttered with lots of things and colours on the page. Content providers should use simple clear design when producing content.
- Decorative text. Text should also follow the accessible formatting explained earlier in the Visual impairment section to make it easier to read.